Reading time: 10 minutes | Last updated: August 15, 2025
In today’s digital economy, APIs are the connective tissue that enables rapid innovation and seamless customer experiences. Yet many organizations find their valuable mainframe business logic locked away in COBOL programs that can’t easily integrate with modern applications.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the complete process of exposing mainframe functionality as modern REST APIs, from initial planning through production deployment. Whether you’re integrating with mobile apps, cloud services, or building microservices architectures, this step-by-step approach will help you unlock your mainframe’s potential.
- The Business Case
- Essential Tools and Technologies
- Step-by-Step Implementation Process
- Performance Optimization Strategies
- Real-World Implementation Example
- Testing and Validation Framework
- Going Live: Deployment Best Practices
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Business Case
Modern businesses require real-time data access and instant transaction processing to compete effectively. Traditional mainframe access methods—batch processing, terminal emulation, and file transfers—simply can’t meet today’s digital demands.
Key Business Drivers:
- Customer expectations: Sub-second response times for mobile banking, insurance claims, and e-commerce
- Digital transformation: Integration with cloud services, analytics platforms, and third-party systems
- Developer productivity: Modern development teams expect RESTful APIs with JSON payloads
- Competitive advantage: Faster time-to-market for new features and services
Technical Benefits
API enablement transforms mainframes from isolated systems into integration hubs:
- Real-time access to critical business data and transactions
- Standardized interfaces that modern applications can easily consume
- Reduced MIPS consumption through efficient, targeted API calls
- Improved system resilience with proper error handling and retry logic
- Enhanced monitoring and observability for business-critical processes
Common Use Cases
- Mobile banking apps accessing account balances and transaction history
- Insurance portals processing claims and policy updates in real-time
- E-commerce platforms validating customer credit and processing payments
- Analytics systems consuming transactional data for real-time reporting
- Third-party integrations with CRM, ERP, and marketing automation platforms
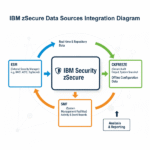
Essential Tools and Technologies
Core API Enablement Platforms
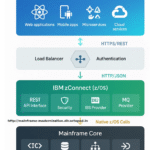
1. IBM API Connect
Best for: Enterprise-grade API management with comprehensive mainframe integration
Key Features:
- Direct CICS transaction integration
- Built-in security and rate limiting
- API lifecycle management
- Developer portal for API documentation
- Analytics and monitoring dashboards
Typical Implementation Cost: $50,000-200,000 annually
2. Zowe API Mediation Layer
Best for: Open-source approach with strong community support
Key Features:
- z/OS native integration
- REST API creation from existing services
- Single sign-on capabilities
- Extensible plugin architecture
- No licensing costs
Implementation Complexity: Medium to High
3. CA API Gateway (Broadcom)
Best for: Organizations already invested in CA/Broadcom ecosystem
Key Features:
- Mainframe connector capabilities
- Enterprise security features
- High-performance throughput
- Integration with CA monitoring tools
4. MuleSoft Anypoint Platform
Best for: Hybrid integration scenarios with multiple systems
Key Features:
- Mainframe connectivity through specialized connectors
- Visual API design interface
- Strong data transformation capabilities
- Cloud and on-premises deployment options
Supporting Technologies
Message Queuing:
- IBM MQ for reliable, asynchronous communication
- Apache Kafka for high-throughput event streaming
- RabbitMQ for flexible routing and delivery patterns
Data Transformation:
- IBM DataStage for complex data mapping
- Talend for open-source ETL capabilities
- Custom transformation services for specialized requirements
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
Phase 1: Discovery and Planning (Weeks 1-2)
1.1 Application Inventory
Create a comprehensive catalog of your mainframe applications:
Application Assessment Template:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Application: Customer Account Management │
│ CICS Transaction: ACCT001 │
│ Business Function: Account balance inquiry │
│ Input: Account number (9 digits) │
│ Output: Balance, status, last transaction │
│ Usage Frequency: 50,000 calls/day │
│ Business Priority: Critical │
│ API Complexity: Low │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘1.2 API Design Planning
For each transaction, define the REST API specification:
Example API Specification:
json
{
"endpoint": "/api/v1/accounts/{accountNumber}/balance",
"method": "GET",
"authentication": "OAuth 2.0 Bearer Token",
"rate_limit": "1000 requests/minute",
"response_format": {
"accountNumber": "string",
"balance": "decimal",
"currency": "string",
"lastTransactionDate": "ISO 8601 datetime",
"status": "string"
}
}1.3 Security Requirements Assessment
Document security and compliance requirements:
- Authentication methods (OAuth 2.0, API keys, certificates)
- Authorization levels (read-only, transaction capabilities)
- Data encryption requirements (in-transit and at-rest)
- Compliance standards (PCI-DSS, SOX, GDPR)
- Audit logging specifications
Phase 2: Environment Setup (Weeks 2-3)
2.1 Development Environment Configuration
IBM API Connect Setup:
- Install API Connect on your chosen platform (cloud or on-premises)
- Configure connectivity to your mainframe LPAR
- Set up development catalogs and organizations
- Create developer accounts and access permissions
Zowe Installation:
- Install Zowe on z/OS following official documentation
- Configure the API Mediation Layer
- Set up authentication services (SAF integration)
- Install and configure CLI tools
2.2 Network and Security Configuration
Network Architecture:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Client │───▶│ API Gateway │───▶│ Mainframe │
│Applications │ │ │ │ CICS │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
HTTPS TLS APPC/TCPKey Configuration Steps:
- Configure TLS certificates for secure communication
- Set up firewall rules for API gateway access
- Implement network segmentation for security
- Configure load balancers for high availability
Phase 3: API Development (Weeks 3-6)
3.1 COBOL-to-REST API Conversion
Step 1: Analyze COBOL Copybook
cobol
01 ACCOUNT-REQUEST.
05 ACCT-NUMBER PIC 9(9).
05 REQUEST-TYPE PIC X(2).
01 ACCOUNT-RESPONSE.
05 ACCT-NUMBER PIC 9(9).
05 ACCOUNT-BALANCE PIC S9(13)V99 COMP-3.
05 ACCOUNT-STATUS PIC X(1).
05 LAST-TRANS-DATE PIC X(8).
05 RESPONSE-CODE PIC X(2).Step 2: Create Data Mapping
json
{
"input_mapping": {
"accountNumber": "ACCT-NUMBER",
"requestType": "REQUEST-TYPE"
},
"output_mapping": {
"accountNumber": "ACCT-NUMBER",
"balance": "ACCOUNT-BALANCE / 100",
"status": "ACCOUNT-STATUS",
"lastTransactionDate": "format_date(LAST-TRANS-DATE)",
"responseCode": "RESPONSE-CODE"
}
}Step 3: Implement API Endpoint
Using IBM API Connect, create the API definition:
yaml
swagger: '2.0'
info:
title: Account Balance API
version: 1.0.0
paths:
/accounts/{accountNumber}/balance:
get:
parameters:
- name: accountNumber
in: path
required: true
type: string
pattern: '^[0-9]{9}$'
responses:
'200':
description: Account balance retrieved successfully
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/AccountBalance'
'404':
description: Account not found
'500':
description: Internal server error3.2 Error Handling Implementation
COBOL Error Code Mapping:
json
{
"error_mappings": {
"00": {"http_code": 200, "message": "Success"},
"01": {"http_code": 404, "message": "Account not found"},
"02": {"http_code": 403, "message": "Account access denied"},
"99": {"http_code": 500, "message": "System error"}
}
}Phase 4: Security Implementation
4.1 OAuth 2.0 Configuration
Client Credentials Flow Implementation:
json
{
"oauth_config": {
"grant_type": "client_credentials",
"token_endpoint": "https://api.yourbank.com/oauth/token",
"scope": "account:read",
"token_expiry": 3600
}
}API Gateway Security Policy:
xml
<policy>
<oauth>
<scope>account:read</scope>
<validate-token>true</validate-token>
</oauth>
<rate-limit>
<requests-per-minute>1000</requests-per-minute>
</rate-limit>
</policy>4.2 Data Encryption and Transport Security
TLS Configuration:
- Use TLS 1.3 for all API communications
- Implement certificate pinning for mobile applications
- Configure proper cipher suites and key exchange methods
- Set up certificate rotation procedures
Field-Level Encryption for Sensitive Data:
json
{
"encrypted_fields": ["accountNumber", "balance"],
"encryption_algorithm": "AES-256-GCM",
"key_management": "AWS KMS"
}Performance Optimization Strategies
Connection Pooling and Resource Management
CICS Connection Pool Configuration:
xml
<cics-connection-pool>
<initial-connections>10</initial-connections>
<max-connections>50</max-connections>
<connection-timeout>30000</connection-timeout>
<idle-timeout>300000</idle-timeout>
</cics-connection-pool>Caching Strategies
Multi-Level Caching Architecture:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Application │───▶│ CDN │───▶│ API Gateway │
│ Cache │ │ (Edge) │ │ Cache │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Mainframe │
│ CICS │
└─────────────┘Cache Configuration Examples:
json
{
"cache_policies": {
"account_balance": {
"ttl": 300,
"cache_key": "balance:{accountNumber}",
"invalidation_events": ["transaction_posted"]
},
"customer_profile": {
"ttl": 3600,
"cache_key": "profile:{customerId}",
"invalidation_events": ["profile_updated"]
}
}
}Asynchronous Processing
For Long-Running Operations:
json
{
"async_pattern": {
"initial_response": {
"status": "processing",
"request_id": "12345",
"callback_url": "/api/v1/status/12345"
},
"status_check": {
"endpoint": "/api/v1/status/{requestId}",
"polling_interval": 5000
}
}
}Real-World Implementation Example
Case Study: Regional Bank Account Balance API
Business Requirement: Create a real-time account balance API for mobile banking application serving 500,000 customers.
Technical Specifications:
- Peak Load: 10,000 concurrent requests
- Response Time: < 200ms (95th percentile)
- Availability: 99.9% uptime
- Security: OAuth 2.0 with rate limiting
Implementation Architecture
Mobile App ──HTTPS──▶ Load Balancer ──▶ API Gateway Cluster
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────┐
│ Cache Layer │
│ (Redis Cluster - 99% hits) │
└─────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼ (1% cache miss)
┌─────────────────────────────────┐
│ CICS Connection Pool │
│ (50 connections) │
└─────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────┐
│ Mainframe z/OS LPAR │
│ COBOL Program: ACCTBAL │
└─────────────────────────────────┘Performance Results
Before API Implementation:
- Batch file processing: 4-hour delay for balance updates
- Terminal-based access: 30-second response times
- Limited to business hours operation
After API Implementation:
- Real-time balance access: Average 50ms response time
- 99% cache hit ratio reducing mainframe load
- 24/7 availability with 99.97% uptime achieved
- 40% reduction in MIPS consumption
Code Example: Complete API Implementation
API Definition (OpenAPI 3.0):
yaml
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: Banking Account API
version: 1.0.0
description: Real-time account balance and transaction services
paths:
/api/v1/accounts/{accountNumber}/balance:
get:
summary: Get account balance
parameters:
- name: accountNumber
in: path
required: true
schema:
type: string
pattern: '^[0-9]{9}$'
security:
- OAuth2: [account:read]
responses:
'200':
description: Balance retrieved successfully
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
accountNumber:
type: string
balance:
type: number
format: decimal
currency:
type: string
example: "USD"
asOfDate:
type: string
format: date-time
status:
type: string
enum: [ACTIVE, CLOSED, FROZEN]Testing and Validation Framework
Automated Testing Strategy
1. Unit Testing for API Logic
javascript
// API Gateway Logic Testing
describe('Account Balance API', () => {
it('should return valid balance for existing account', async () => {
const response = await request(app)
.get('/api/v1/accounts/123456789/balance')
.set('Authorization', 'Bearer valid_token')
.expect(200);
expect(response.body.balance).toBeDefined();
expect(response.body.accountNumber).toBe('123456789');
});
});2. Integration Testing with Mainframe
json
{
"test_scenarios": [
{
"name": "Valid Account Balance Request",
"input": {"accountNumber": "123456789"},
"expected_cics_call": "ACCTBAL",
"expected_response": {
"balance": 1234.56,
"status": "ACTIVE"
}
},
{
"name": "Invalid Account Number",
"input": {"accountNumber": "000000000"},
"expected_cics_response": "01",
"expected_http_status": 404
}
]
}3. Performance Testing
yaml
# JMeter Test Plan
load_test:
concurrent_users: 1000
ramp_up_time: 60
test_duration: 600
target_response_time: 200ms
success_criteria:
- response_time_95th_percentile < 200ms
- error_rate < 0.1%
- throughput > 5000 TPSProduction Readiness Checklist
Security Validation ✅
- OAuth 2.0 token validation working correctly
- Rate limiting configured and tested
- TLS certificates installed and configured
- API access logs capturing required information
- Penetration testing completed
Performance Validation ✅
- Load testing completed at expected peak capacity
- Cache hit ratios meeting targets (>95%)
- CICS connection pools properly configured
- Response times meeting SLA requirements
- Monitoring and alerting configured
Operational Readiness ✅
- API documentation published to developer portal
- Support procedures documented and tested
- Rollback procedures tested and documented
- Monitoring dashboards configured
- Incident response procedures established
Going Live: Deployment Best Practices
Phased Rollout Strategy
Phase 1: Internal Testing (Week 1)
- Deploy to development environment
- Conduct integration testing with sample data
- Validate security controls and monitoring
Phase 2: Pilot Deployment (Week 2)
- Deploy to limited production environment
- Enable API for 5% of user base
- Monitor performance and error rates closely
Phase 3: Gradual Rollout (Weeks 3-4)
- Increase user base to 25%, then 50%, then 100%
- Monitor key metrics at each stage
- Have rollback plan ready at each step
Monitoring and Observability
Key Metrics to Track:
json
{
"api_metrics": {
"response_time": "Average, 95th percentile, max",
"throughput": "Requests per second",
"error_rate": "Percentage of failed requests",
"cache_hit_ratio": "Percentage of cache hits vs misses"
},
"mainframe_metrics": {
"cics_response_time": "Transaction response time",
"connection_pool_usage": "Active connections / total connections",
"mips_consumption": "MIPS usage attributed to API calls"
}
}Alerting Thresholds:
- Response time > 200ms for 5 consecutive minutes
- Error rate > 0.5% for 2 consecutive minutes
- Cache hit ratio < 90% for 10 consecutive minutes
- CICS connection pool > 80% utilization
Success Metrics and KPIs
Technical KPIs:
- API Response Time: < 200ms (95th percentile)
- Availability: > 99.9% uptime
- Error Rate: < 0.1%
- Cache Hit Ratio: > 95%
Business KPIs:
- MIPS Reduction: 30-40% decrease in mainframe resource usage
- Development Velocity: 50% faster feature delivery
- Customer Satisfaction: Improved app store ratings
- Revenue Impact: Increased mobile banking adoption
Key Takeaways
Successful mainframe API modernization requires careful planning, proper tooling, and a systematic implementation approach:
- Start with high-value, low-complexity transactions to build momentum and learn
- Invest heavily in security and performance testing – these are non-negotiable for production systems
- Implement comprehensive monitoring from day one to ensure ongoing success
- Plan for scalability – successful APIs often exceed initial usage projections
- Document everything – API specifications, security policies, and operational procedures
The transformation from isolated COBOL programs to modern REST APIs opens unprecedented possibilities for innovation while preserving the reliability and performance that made mainframes indispensable.
Ready to begin your mainframe API modernization journey? Start with a pilot project focusing on a single, well-understood business transaction, and use the lessons learned to scale your approach across your entire application portfolio.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does it typically take to implement a mainframe API? A: For a simple CICS transaction, expect 2-4 weeks from planning to production. Complex APIs with multiple integrations may take 6-12 weeks.
Q: What’s the performance impact on the mainframe? A: Well-designed APIs typically reduce MIPS consumption by 30-40% compared to traditional access methods, due to more efficient data requests and caching.
Q: Can we implement APIs without changing existing COBOL programs? A: Yes, most API modernization approaches work with existing COBOL programs unchanged, using integration middleware to handle the API translation.
Q: What’s the typical ROI timeline for mainframe API projects? A: Organizations typically see positive ROI within 6-12 months through reduced development costs, improved system efficiency, and new revenue opportunities.
This guide provides practical implementation guidance for mainframe API modernization. For specific technical implementation details and architecture decisions, consult with certified mainframe and API integration specialists.










Thank you so much for this excellent piece! We are currently going through mainframe modernization and, honestly, we are quite desperate to find a good strategy that works. Your insights are really precious for us!